GRIPPER SOLUTIONS.
The simple version of our Indumatik systems requires a main gripper to pick up pallets, workpieces or tools. The gripper then picks up the pallet, for example, and moves it to the machining center for processing.
The main gripper can only perform one of these tasks. Depending on the expansion stage and the desired flexibility of the Indumatik, additional grippers are used, which are then inserted into the main gripper as sub-grippers.
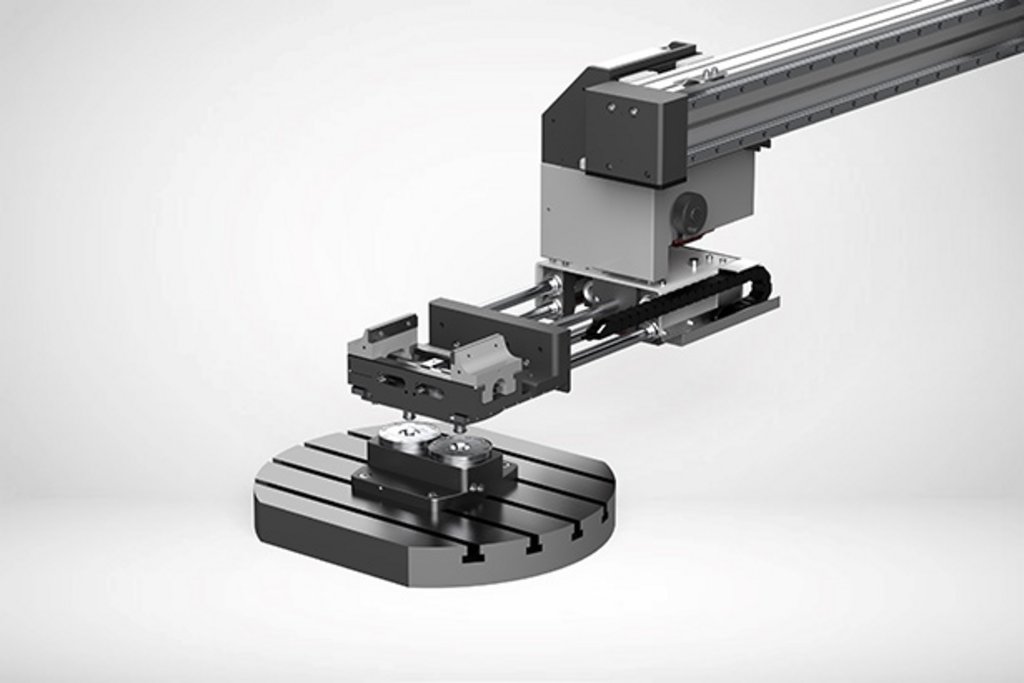

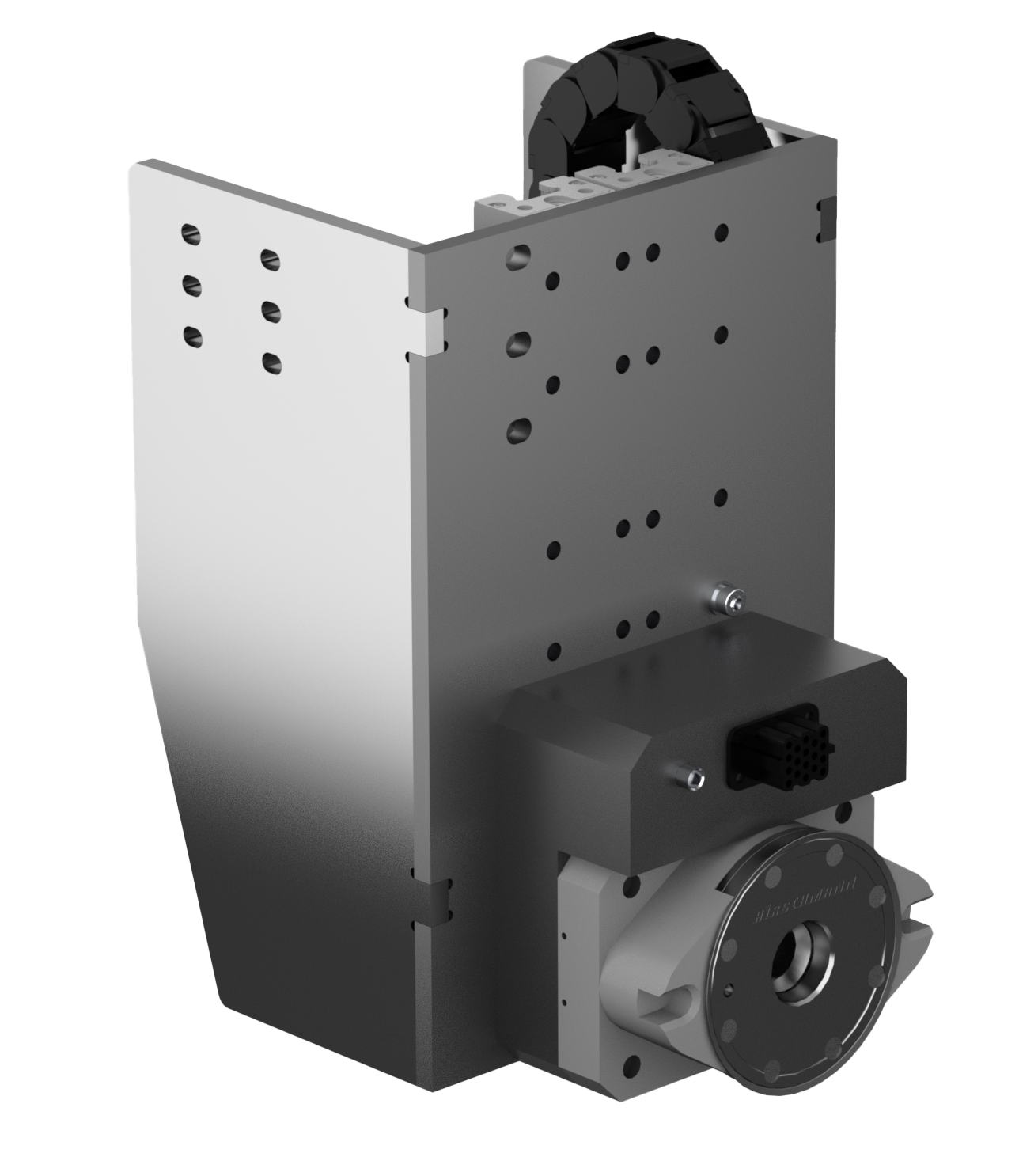
ZERO POINT GRIPPER.
The zero-point gripper is a component of many standardized Indumatik systems. The zero-point gripper picks up pallets as standard and moves them into the machining center for processing. The maximum handling weight is 200 kg. The zero-point gripper is also used as an interface to various sub-grippers. In this case, compressed air and energy / sensors (media) are transferred from the main gripper (zero-point gripper) to the sub-gripper.

FORK LIFT.
The fork gripper is often used in Indumatik pallet systems to transport heavy weights of up to 500 kg. The fork gripper moves under the pallet and lifts it out for transportation.

FORK GRIPPER (SMALL).
The "small" fork gripper is used either for handling small pallets or for handling vices and is used for handling weights of up to 30 kg. The gripper forks are passive and cannot be adjusted. This fork gripper moves directly into the pallet and lifts it out for transportation.

PARALLEL GRIPPERTOOL GRIPPER.
The parallel gripper is an active element and is used in the Indumatik Toolchanger, for example, to pick up the tools in the rack and then make them available to the machine. When moved into position, the gripper fingers are opened and closed by a few millimetres to safely pick up the tool for transport. The stroke is pneumatic and is monitored by sensors in the end positions.

DOUBLE GRIPPER (PARALLEL).
The double gripper is usually designed as a double parallel gripper. The advantage of this gripper is the quick changeover. A tool or workpiece is removed from the machine with a single movement and a new one is fed in with a short rotary movement. This significantly reduces changeover times and increases the productivity of the system.
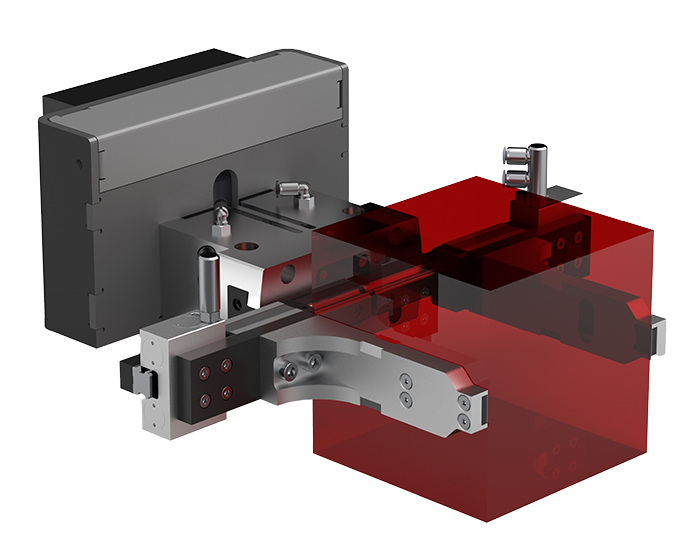
GRIPPER PREMIUM.
The gripper Premium is a passive element that is mainly used for workpiece handling in conjunction with an articulated arm robot in the Indumatik VR 70. The gripper fingers are adjusted independently to the next workpiece size. This means that different workpiece sizes and components can be produced unmanned overnight in an Indumatik VR 70 without the need for a skilled worker to intervene.
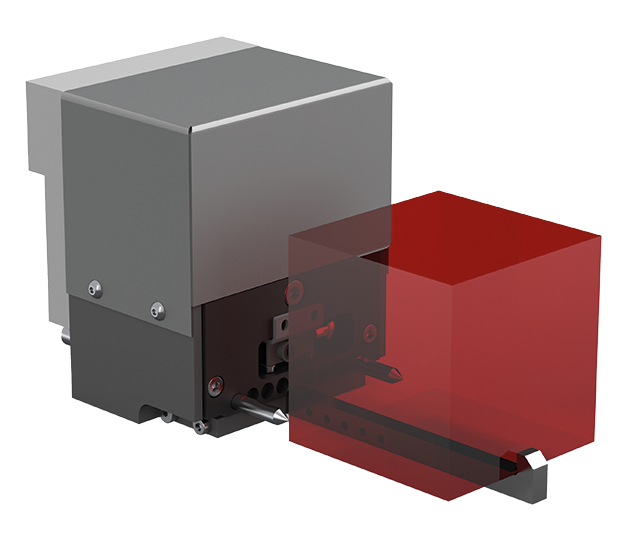
GRIPPER BASIC.
The Basic gripper is a passive element with independent adjustment of the opening path in the Indumatik. This gripper handles workpieces and is mainly used in conjunction with linear axis robots in the Indumatik VL 40 and Indumatik VL 80 as well as with articulated arm robots in the Indumatik 200. The adjustment to the next workpiece size is independent. This means that different workpiece sizes and components can be produced unmanned overnight in these systems without the need for a skilled worker to intervene.
PALLET HANDLING.
Workpieces are clamped on pallets and stored and retrieved with the pallet in the machining center. The flexible production system is ideal for small quantities or heavy handling weights and makes it possible to automate almost all clamping systems.
PARTS HANDLING.
The pallet is not required for parts handling. The workpiece or finished part is fed directly into the machining center with a gripper. This type of automatic machine feed is recommended for large quantities with low weight.